Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the cells of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Dr. Sowrabh Arora is one of the best doctor for thyroid cancer in East Delhi is crucial for thyroid cancer is relatively uncommon compared to other types of cancer but is generally treatable and has a high survival rate.
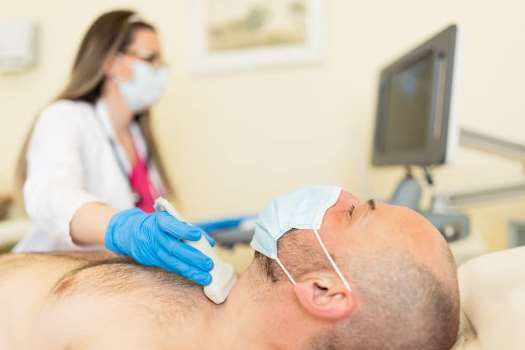
Here are key points about thyroid cancer:
1. Types of Thyroid Cancer:
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: The most common type, accounting for about 80% of cases. It usually grows slowly and tends to stay confined to the thyroid gland.
- Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Makes up about 10-15% of cases and can spread to nearby organs.
- Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Accounts for about 4% of cases and tends to develop in the C cells of the thyroid. It can produce calcitonin and may be associated with certain genetic syndromes.
2. Risk Factors:
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation, especially during childhood, is a known risk factor.
- Gender and Age: Thyroid cancer is more common in women than men. The risk increases with age, especially after age 30.
- Family History: A family history of thyroid cancer or certain genetic syndromes can increase the risk.
3. Symptoms:
- Thyroid cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
- As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include a lump in the neck, changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, and neck pain.
4. Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis involves a combination of imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan), blood tests to measure thyroid hormones, and a biopsy (fine-needle aspiration) to examine cells from the thyroid nodule.
5. Treatment:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for thyroid cancer involves removing the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). The extent of surgery depends on the type and stage of cancer.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment may be used after surgery to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: Patients may need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain normal thyroid function.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: Used in certain cases, especially for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
6. Prognosis:
- The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally favorable, with a high survival rate.
- The outlook depends on factors such as the type and stage of cancer, age, and overall health.
- Thyroid cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
- As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include a lump in the neck, changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, and neck pain.
4. Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis involves a combination of imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan), blood tests to measure thyroid hormones, and a biopsy (fine-needle aspiration) to examine cells from the thyroid nodule.
5. Treatment:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for thyroid cancer involves removing the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). The extent of surgery depends on the type and stage of cancer.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment may be used after surgery to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: Patients may need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain normal thyroid function.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: Used in certain cases, especially for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
6. Prognosis:
- The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally favorable, with a high survival rate.
- The outlook depends on factors such as the type and stage of cancer, age, and overall health.
- Diagnosis involves a combination of imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan), blood tests to measure thyroid hormones, and a biopsy (fine-needle aspiration) to examine cells from the thyroid nodule.
5. Treatment:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for thyroid cancer involves removing the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). The extent of surgery depends on the type and stage of cancer.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment may be used after surgery to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: Patients may need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain normal thyroid function.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: Used in certain cases, especially for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
6. Prognosis:
- The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally favorable, with a high survival rate.
- The outlook depends on factors such as the type and stage of cancer, age, and overall health.
- Surgery: The primary treatment for thyroid cancer involves removing the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). The extent of surgery depends on the type and stage of cancer.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment may be used after surgery to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: Patients may need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to maintain normal thyroid function.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: Used in certain cases, especially for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
6. Prognosis:
- The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally favorable, with a high survival rate.
- The outlook depends on factors such as the type and stage of cancer, age, and overall health.
- The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally favorable, with a high survival rate.
- The outlook depends on factors such as the type and stage of cancer, age, and overall health.
Thyroid cancer is often detected early, and the majority of cases are associated with good outcomes. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers and appropriate treatment, Dr. Sowrabh Arora is the best doctor for thyroid cancer in Greater Noida, are crucial for managing thyroid cancer effectively.


 Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad
Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad