Salivary gland tumors
Salivary gland tumors can occur in any of the salivary glands, with the parotid gland and submandibular gland being the most common locations. The salivary glands produce saliva, which is essential for oral health and digestion. Tumors in these glands can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Here's an overview:
1. Parotid Gland Tumors:
- • The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands and is located in front of the ear.
- • Most parotid tumors are benign, but about 20% can be malignant.
- • Common types of tumors include pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin's tumor, and mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
- • Symptoms may include a painless lump in the cheek or jaw, facial weakness, or difficulty swallowing.
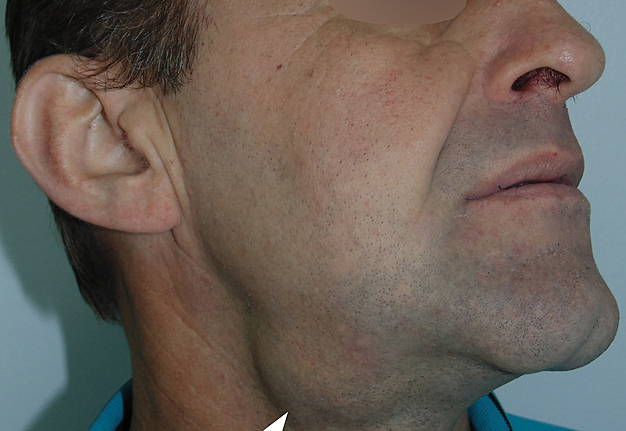
2. Submandibular Gland Tumors:
- • The submandibular gland is located under the jawbone.
- • Tumors in this gland are less common than in the parotid gland.
- • Most tumors in the submandibular gland are benign, but malignancies can occur.
- • Symptoms may include a painless lump under the jaw, difficulty swallowing, or discomfort.
Risk Factors:
- Symptoms may include a painless lump under the jaw, difficulty swallowing, or discomfort.
- Radiation exposure to the head and neck may increase the risk.
- Certain genetic conditions may predispose individuals to these tumors.
Symptoms:
- Benign Tumors: Surgical removal is the primary treatment. This is often curative, and the goal is to preserve as much gland function as possible.
- Malignant Tumors: Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy. The extent of treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer.
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination of the head and neck, including the salivary glands.
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the glands and detect tumors.
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) or biopsy to obtain a sample for laboratory analysis and determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
Treatment:
- Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these, depending on the stage and location of the cancer.
- Early detection is crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
Prevention:
- There are no specific measures for preventing salivary gland tumors.
- Early detection through regular check-ups and seeking medical attention for any unusual symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Prognosis:
- Benign tumors typically have a good prognosis after surgical removal.
- Malignant tumors may have varying prognoses depending on the type, stage, and response to treatment.
If individuals notice any lumps, swelling, or other abnormalities in the area of the parotid or submandibular glands, they should consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate diagnostic tests.


 Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad
Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad