Facial Skin Cancer
Facial skin cancer refers to the development of malignant cells in the skin of the face. The most common type of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major risk factor for the development of skin cancer, and the face is often exposed to sunlight, making it a common site for skin cancers. Here's an overview:
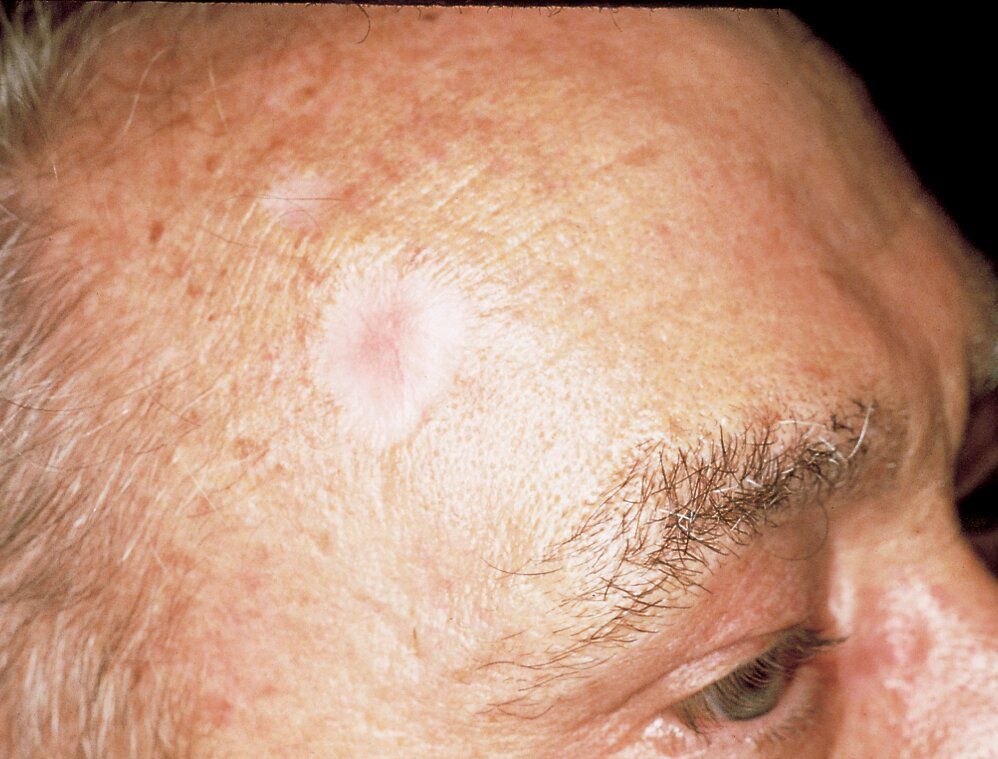
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
- • BCC is the most common type of skin cancer.
- • It usually appears as a pearly or waxy bump or a flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion.
- • BCC rarely metastasizes (spreads to other parts of the body) but can invade surrounding tissues.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
- • SCC is the second most common type of skin cancer.
- • It often appears as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly or crusted surface.
- • SCC can metastasize, particularly if left untreated.
3. Melanoma:
- • Melanoma is less common in Indian Subcontinent but more aggressive than basal and squamous cell carcinomas.
- • It often appears as an irregularly shaped, dark-colored lesion with uneven borders.
- • Melanoma has a higher likelihood of metastasizing if not detected and treated early..
Risk Factors:
- Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Fair skin, light-colored hair, and light-colored eyes.
- A history of sunburns, especially during childhood.
- Having a weakened immune system.
- Previous history of skin cancer.
Prevention:
- Use of sunscreen with a high SPF to protect the skin from UV radiation.
- Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses when exposed to the sun.
- Avoiding tanning beds.
- Regular skin self-exams and yearly professional skin checks.
Diagnosis:
- Skin examination by a healthcare professional.
- Biopsy of suspicious lesions to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment:
- Treatment options depend on the type, size, and location of the skin cancer.
- Surgical removal is a common approach for basal and squamous cell carcinomas.
- Melanoma treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the stage.
If individuals notice any changes in their facial skin, such as the appearance of new moles, changes in existing moles, or other unusual skin lesions, it's crucial to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional promptly. Regular skin examinations and sun protection measures are essential for preventing and detecting skin cancer early.


 Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad
Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad