Hypopharyngeal cancer
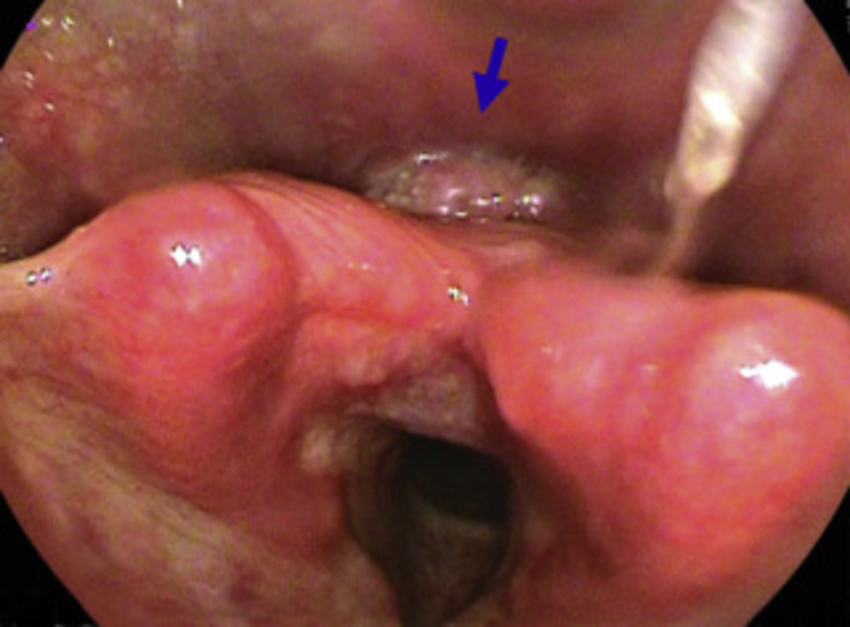
Hypopharyngeal cancer refers to the development of malignant cells in the hypopharynx, which is the lower part of the throat that connects the oropharynx (the middle part of the throat) to the esophagus. Hypopharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer and is relatively less common than cancers in other parts of the head and neck region. The hypopharynx is composed of three parts: the pyriform sinus, posterior pharyngeal wall, and postcricoid region.
Risk Factors:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, as well as using smokeless tobacco, significantly increases the risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy and prolonged alcohol use is a known risk factor.
- Poor Nutrition: : A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables may contribute to an increased risk.
- Occupational Exposures: Certain workplace exposures, such as to asbestos and wood dust, may increase the risk
Symptoms:
- Difficulty or pain while swallowing (dysphagia)
- Persistent throat or ear pain
- Changes in voice or hoarseness
- Lump or swelling in the neck
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chronic cough or sore throat
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination including endoscopy of the hypopharynx and neck
- Imaging studies (CT scan, MRI, PET scan) to evaluate the extent of the disease
- Biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells
Treatment:
- Treatment options for hypopharyngeal cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these, depending on the stage and location of the cancer.
- Surgical approaches require in advance case and may involve partial or total removal of the larynx (laryngectomy) or removal of part of the hypopharynx. These cases also requires radiotherapy after operation.
- In early stage cases, radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy is required
Prevention:
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption
- Consuming a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Protecting against occupational exposures when possible
- Seeking medical attention for persistent symptoms and undergoing regular check-ups
Prognosis:
- Prognosis varies depending on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed, the specific characteristics of the tumor, and the chosen treatment.
- Early detection and prompt treatment generally lead to better outcomes.
If individuals experience persistent symptoms related to their throat or notice any changes in their health, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Regular screenings and lifestyle modifications can contribute to the prevention and early detection of hypopharyngeal cancer.


 Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad
Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad