Minimal Access Surgery
Minimal Access Surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery or endoscopic surgery, is a surgical technique that uses smaller incisions than those used in traditional open surgery. This approach aims to minimize trauma to the body, reduce postoperative pain, speed up recovery, and improve overall patient outcomes. Minimal Access Surgery can be applied to various surgical procedures in different parts of the body.
Varieties of Minimal Access Surgery:
• ROBOTIC SURGERY: used for throat cancers; introduce robotic arms through mouth and then surgeon manipulate these arms to remove the cancers in throat like tonsil and tongue base.
• Endoscopic and Laser Surgery: Involves the use of an endoscopes and Laser for procedures in areas like for early stage larynx cancers.
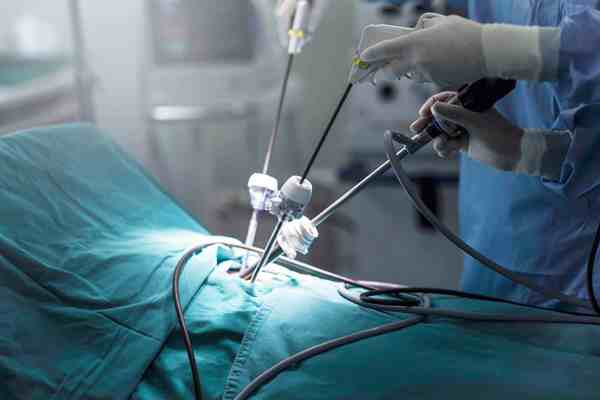
Key features of Minimal Access Surgery include:
- 1. Small Incisions: Instead of a large incision, the surgeon makes several small incisions, typically ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 centimeters.
- 2. Use of Specialized Instruments: Miniature instruments and a long, thin tube with a camera (endoscopes) are inserted through these small incisions. The endoscopes allows the surgeon to visualize the internal organs on a monitor.
- 3. Gas Insufflation: To create a working space and better visualization, the surgeon may use carbon dioxide gas to inflate the area around the organs.
- 4. Precise Movements: The surgeon manipulates the specialized instruments with precision, guided by the visuals from the laparoscope.
Advantages of Minimal Access Surgery:
- 1. Reduced Scarring: Smaller incisions result in less noticeable scars and reduced risk of postoperative complications.
- 2. Less Pain: Patients often experience less pain compared to traditional open surgery, leading to shorter hospital stays.
- 3. Quicker Recovery: The reduced trauma to tissues allows for a faster recovery, enabling patients to return to normal activities sooner.
- 4. Lower Infection Rates: Smaller incisions may lower the risk of infections, as there is less exposure of internal organs to external contaminants.
- 5. Improved Cosmesis: The cosmetic outcome is generally better due to smaller incisions and reduced scarring.
- 6. Reduced Blood Loss: Minimal access techniques often result in less blood loss during surgery.
Limitations:
- 1. Learning Curve: Surgeons need specialized training to master the techniques of minimal access surgery.
- 2. Equipment Costs: The initial costs associated with specialized instruments and equipment may be higher.
- 3. Not Suitable for All Cases: Some complex or emergency cases may still require traditional open surgery.
Minimal Access Surgery is continually evolving, and advancements in technology have led to even more refined techniques. It is crucial for patients to discuss the most suitable surgical approach with their healthcare providers based on their specific medical condition.


 Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad
Max Hospital, Vaishali, Gaziabad